Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Caviarlieri | Published November 09, 2020
Do you feel tired all the time and you do not know why? You may then be suffering from Chronic Fatigue Syndrome.
Chronic fatigue syndrome, also known as myalgia encephalomyelitis, is a complicated illness characterized by at least six months of extreme fatigue that is not relieved by rest. In addition you may also suffer from a collective group of other additional symptoms that may last for at least six months.
For most people suffering from chronic fatigue syndrome, the disorder begins very suddenly, often following a flu like infection or an episode of physical or psychological trauma, such as a surgery or a traumatic accident. In other cases, chronic fatigue syndrome develops gradually. The illness lasts for many months or years, and only a small percentage of people do fully recover.
The problem is that no known cause for chronic fatigue syndrome has been identified. However there is now growing evidence that some patients with chronic fatigue syndrome may have an autoimmune condition which is a condition when their own immune system attacks particular tissues in the body.
Patients with chronic fatigue syndrome may also suffer as a result of defects in the ability of the cells in their bodies to make energy. Although the illness is most common in people 25 to 45 years old, chronic fatigue syndrome can attack people of all age groups, including children.
Is Chronic Fatigue Syndrome a Long-Term Effect of COVID 19?
It has been reported recently that a large number of people who contract the coronavirus do not fully recover in a few weeks, and many of them still experience chronic fatigue even after recovery. More than a third of those who have been tested positive for COVID-19 and have symptoms don’t feel like they’re back to normal, even weeks later. One in five of those between the ages 18-34 who had no prior chronic medical conditions say that they have not completely recovered.
In view of this scientists are now beginning to research to ascertain whether the coronavirus also creates post-viral medical problems like chronic fatigue syndrome.
What are the Symptoms of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome?
The most obvious symptom of chronic fatigue syndrome is an unexplained, persistent feeling of tiredness, which cannot be relieved by rest. This fatigue is severe enough to decrease a person’s normal activity level at home, work or school by 50% or more. Most patients who suffer from Chronic Fatigue Syndrome will have at least four of the following symptoms that are present for at least six months:
- Impaired concentration or short-term memory, severe enough to affect routine activities at home, work, school or social functions
- Enlarged lymph nodes (swollen glands) in the neck or underarm area
- Muscle pain
- Pain in several joints, with no redness or swelling
- Sore throat
- Frequent headaches which differ in severity and intensity
- An extreme reaction to exertion: feeling sick or unable to recover after exercise or strenuous activity

People with chronic fatigue syndrome often have other symptoms that are not considered part of the official definition of the illness, such as nausea and difficulty tolerating alcoholic beverages or medicines that act on the brain. Many people also have allergies, such as hay fever (allergic rhinitis) or recurring sinus problems.
About half of the people with chronic fatigue syndrome develop depression in the months and years after their illness starts.
There is no laboratory test or procedure to confirm the diagnosis of chronic fatigue syndrome. Doctors can only diagnose this condition based on whether the patient has the symptoms of the illness and by eliminating other degenerative disease (like cancer, hypothyroidism etc.) that can cause long-lasting fatigue.
What are the Treatment Options for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome?
There is no proven treatment for chronic fatigue syndrome. Both moderate aerobic exercise programs and cognitive behavioural therapy which are designed to change the patients’ beliefs about the condition may help improve the level of functionality. But it is not a cure.
In general, doctors advise their patients a combination of the following:
Lifestylechanges.
Patients are often initially encouraged to slow down, minimize physical exertion and try to avoid psychological stress. They have to learn to conserve their energy for essential activities at home or work and to cut back on less-important activities.
Resuming exercise gradually but steadily.
With the help of a physical therapist, patients have to start an exercise program in which aerobic physical activity begins very slowly, and is increased very gradually. Patients can expect occasionally to feel worse the day after aerobic exercise. If that happens, many doctors recommend avoiding exercise for several days and then resuming a less-intensive exercise program, and slowly increasing the pace.
Treating existing psychiatric problems.
In the approximately 50% to 60% of people with chronic fatigue syndrome who develop depression, antidepressant treatment and talk therapy can be valuable in treating the depression.
Treating existing pain.
Aspirin, acetaminophen (Tylenol) or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to treat headaches, muscle pain and joint pain. Antidepressant medications also may help to reduce chronic pain.
Treating existing allergy symptoms.
Antihistamines and decongestants are used to treat allergy symptoms.
Why is Caviarlieri Useful to Mitigate the Symptoms of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome?
Caviarlieri is a powerful multi-faceted cellular therapy treatment system that is backed by Science. It has several studies published in peer-reviewed journals and the benefit claims are therefore evidence based like significant increase in energy levels, mood elevation, reduction in joint pain, enhancement of sleep quality, improving mental focus, reducing inflammation and supporting immune health. By providing essential nutrition at the cellular level, Caviarlieri triggers protein synthesis and stimulates our own body’s healing system to repair and renew our cells versus the damaged cells. Some of the evidence based benefits which can help improve the symptoms of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome by taking Caviarlieri are:
1. Significant Increase in Energy Levels
All of your body’s energy to function comes from inside your cells and is made in the mitochondria (known as the “powerhouse” of the cell). Healthy mitochondria are therefore the fundamental starting point of good energy and health.
Caviarlieri Swiss Caviar Cellular Therapy Supplement provides effective and essential nutrition at the cellular level, accelerating protein synthesis, thereby energizing our cells in the mitochondria and providing more energy, endurance and stamina.
It is evident from the empirical randomised double blind placebo studies on the key ingredients of Caviarlieri that the unique Caviar DNA and Marine extracts helps to increase cellular energy levels of the clinical subjects at multiple levels as indicated in the following charts:
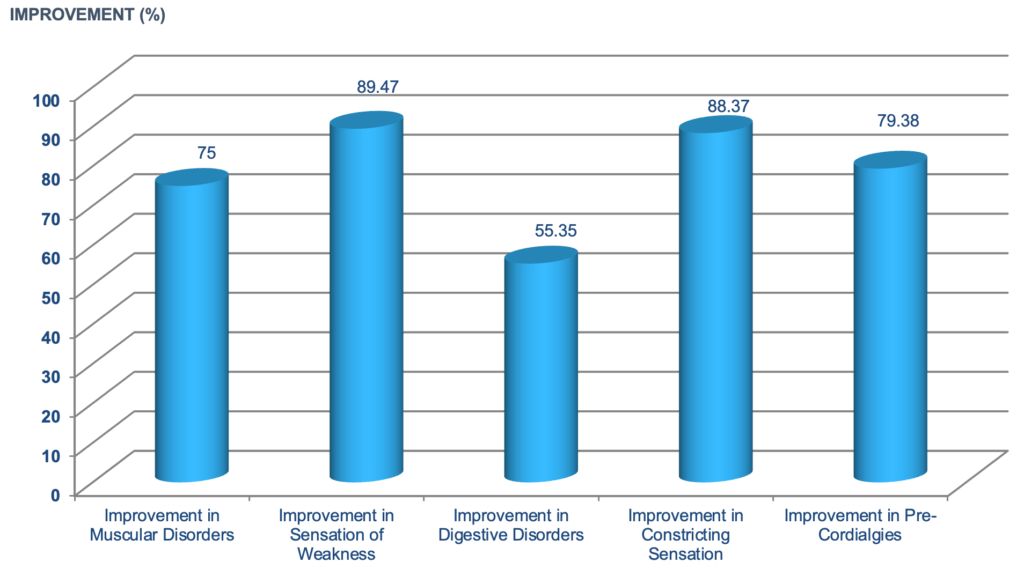
Effects on Physical Fatigue (for clinical subjects with inherent disorders)
People suffering from health issues like muscular weakness disorder, digestive disorder and precordial chest pain etc. will also experience lower energy levels compared to those without such physical disorders.
This study was done comprising 688 people with an average age of 44 years. About 88% of the clinical subjects reported improvements in their physical mobility and 89% in their muscle weakness conditions. With improvements in their physical disorders, the energy levels of the clinical subjects will naturally increase.
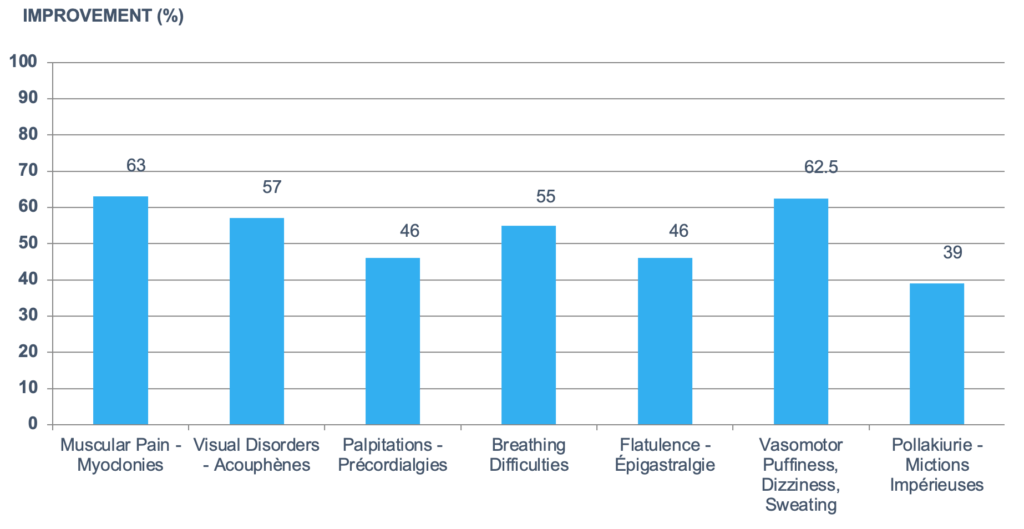
Effects on Physical Symptoms

Physical symptoms or issues like muscular pain, difficulty in breathing, flatulence and incontinence can also adversely affect energy levels.
A study on the ingredients of the Caviar & Marine Cellular DNA Complex on the effect was conducted on 688 clinical subjects (average 44 years) with physical symptoms such as muscular pain, breathing difficulties or dizziness etc. After 15 days, 63% of the subjects reported a reduction in muscular pain and 62.5% reported improvements in vasomotor symptoms like dizziness, night sweats and hot flushes etc.
By improving the physical symptoms of the clinical subjects, their energy levels were enhanced significantly with a reduction in their fatigue levels.
2. Mental Focus & Concentration
Impaired concentration and mental focus is another symptom that is associated with chronic fatigue syndrome. This study was conducted on 688 clinical subjects with an average age of 44 years. The results were measured after 15 days of daily doses of caviar & marine cellular DNA complex (0.8 g/day), key ingredients of Caviarlieri. All clinical subjects reported improvements in the following areas -mental fatigue, memory problems, concentration problems and improvement of memory disorder.76.9% of the clinical subjects reported a significant improvement in concentration.
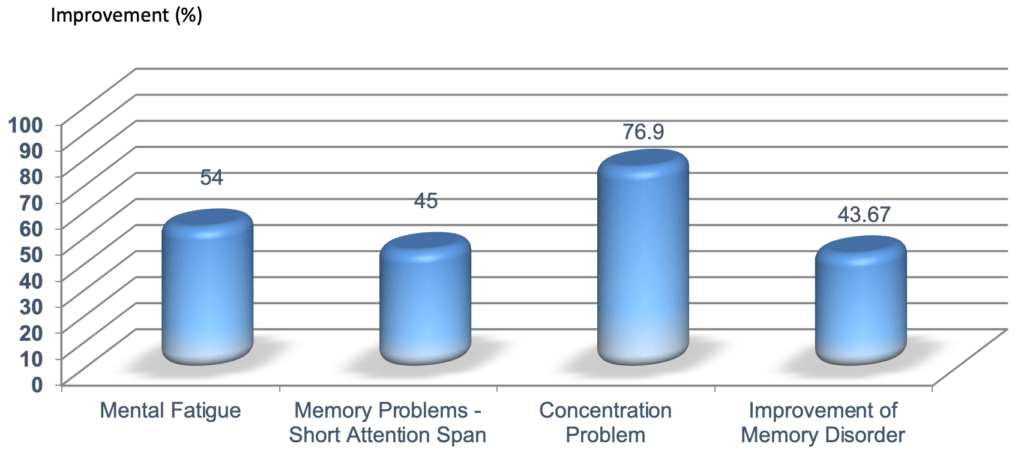
Effect of Caviar & Marine Cellular DNA Complex on Mental Symptoms (688 people – average age = 44 years) after 15 days (daily dose of Caviar & Marine Cellular DNA Complex – 0.8 g/day)
3. Elevate Mild Depression Symptoms – Mood Symptoms

It is known that about 50% of the people who suffer from chronic fatigue syndrome experience depression. In this study, we measured the impact and effectiveness of caviar & marine cellular DNA complex on the following mental symptoms. The study comprised of 688 adults with an average age of 44 years who took daily doses of marine DNA complex for a period of 15 days. 62.88% reported an improvement in mood disorders while 54% showed an improvement in mental fatigue & emotional fear.
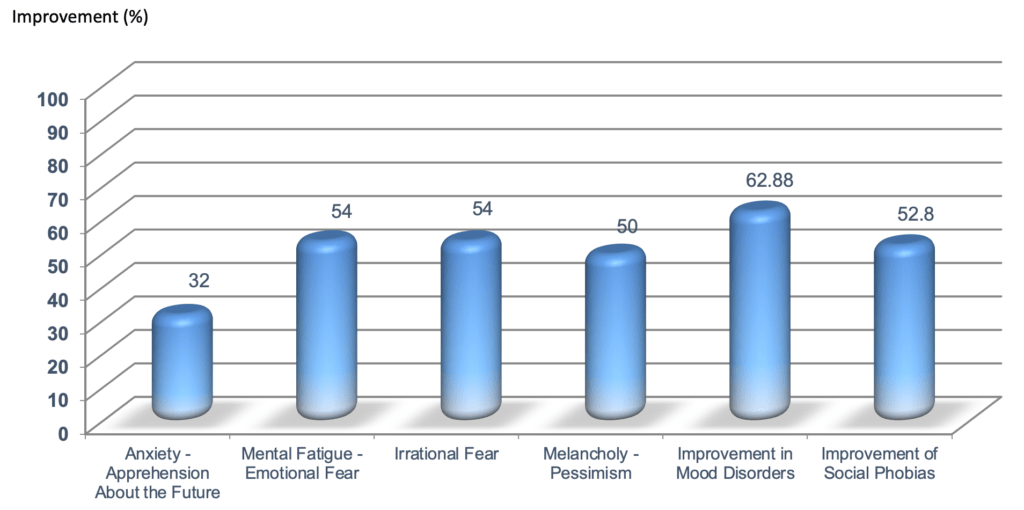
Effect of Caviar & Marine Cellular DNA Complex on Mental Symptoms (688 people – average age = 44 years) after 15 days (daily dose of Caviar & Marine Cellular DNA Complex – 0.8 g/day)
3. Enhance Immune Health
The several clinical studies on the key ingredients of Caviarlieri prove that it has powerful antioxidant properties which can potentially prevent the damage to immune cells by neutralizing free radicals. Free radicals are substances in the environment that can damage cells and reduce immunity. Supplementing the body with Caviarlieri can also help increase the activation of cells which are involved in regulating our immunity.
Free Radical Scavenging Activity Antioxidant Properties
CAVIAR DNA EXTRACT AND MARINE PEPTIDES ON FREE RADICAL FORMATION
(*) Inhibition corresponded to (1 – A CAVIAR CELLULAR DNA COMPLEX). 100(%), where A is the ESR intensity calculated by double integration of low field line.
4. Reduction in Inflammation – Joint pain reduction
Caviarlieri also helps to reduce chronic inflammation as proven in its scientific studies. Many people suffer from chronic inflammation because their immune systems overreact to infection. Chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disease is a condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body. By reducing inflammation, Caviarlieri can help to “regulate” the immune system when it is in overdrive.
Since Caviarlieri has strong anti-inflammatory properties, it will also help reduce joint pain, another symptom associated with chronic fatigue syndrome.
Caviarlieri is a Food Supplement and Not a Drug
There is no known cure for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. The usual treatment protocol to manage the symptoms of this illness involve the use of multiple drugs like antidepressants, aspirin, acetaminophen (Tylenol) or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs,) antihistamines and decongestants etc. However the long term use of these multiple drugs may have adverse side effects and can lead to complications.
Unlike drugs, Caviarlieri is only a nutritional food supplement approved by the Swiss Public Health Authority and it is available in leading Swiss Medical Spas and Medical Centres as well as the prominent pharmacies throughout Switzerland. It has several studies published in peer-reviewed journals demonstrating significant evidence of benefits (as mentioned above) which may help mitigate the symptoms associated with chronic fatigue syndrome without side effects.
Caviarlieri is on the Cologne List® which publishes products which have been tested for selected doping substances by one of the globally-leading laboratories in nutritional supplement analytics.
The efficacy and potency of Caviarlieri is due to its stringent and careful extraction of ingredients and manufacturing. This ensures that all its ingredients reach are absorbed by our body and produce the desired outcome. Caviarlieri is manufactured using our proprietary Swiss Cold Process Extraction Technology, “Cellularix”. Caviarlieri comes in soft gel form which contains encapsulated bioactive nutrients and peptides for optimal absorption. It is important to remember that not everything we consume can be absorbed by the cells in our body.
Subject
Recent Posts
-
The Amazing Benefits of Highly Polymerized Fish Collagen Peptides with Elastin – Caviarlieri
-
The World’s Most Effective Caviar DNA Extract with Marine Bioactive Peptides
-
Are Supplements effective for Joint Pain?
-
Why Is Sustainable Immunity Important for Your Long-Term Health
-
What is your “Body Age” – Biological Age?




