How to Treat and Manage Autoimmune Diseases
Caviarlieri | Published June 24, 2021
A healthy immune system defends our body against disease and infection. But if our immune system malfunctions, it will mistakenly attack our healthy cells, tissues, and organs with severe consequences to our health. This is described as autoimmune disease and these attacks can affect any part of your body, weakening its bodily function and even becoming life-threatening.
There are more than 80 types of known autoimmune diseases, and some have similar symptoms. This makes it hard for your health care provider to know if you really have one of these diseases, and if so, which particular one. Getting a diagnosis can be frustrating and stressful. Often, the first evident symptoms are fatigue, muscle aches and a low fever. The classic sign that you have an autoimmune disease is when your body has inflammation, which can cause redness, heat, pain and swelling in parts of your body. Unfortunately most of these autoimmune diseases have no cure. Some may even require lifelong treatment to ease its symptoms.
The consequence of the disease are have flare-ups, when they get worse, and remissions, when symptoms get better or disappear. Treatment depends on the disease, but in most cases one important goal to avoid the disease is to reduce inflammation in your body.
Most common types of Autoimmune Diseases:
Rheumatoid Arthritis
This autoimmune disorder affects your joints and causes swelling and pain. Over time, the inflammation can damage your cartilage and bones, and you can’t move them as well. RA also can cause problems to your heart and lungs. Medications can help to treat the symptoms and slow the progression and effects of the disease .
Ankylosing Spondylitis
This type of arthritis mostly affects your spine, but it also can affect your chest, neck, hips, and knees. It causes intense pain and stiffness. Your bones might eventually join together and become hard for you to move around. It can affect your organs, too. Your treatment will be physical exercise which may include specific stretches along with medicines to help with pain, DMARDs, and steroid shots. You also might need surgery to replace the damaged joints.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) are kinds of IBD. They result when your body’s defenses attack your intestines and cause inflammation, belly pain, and bleeding. Crohn’s disease usually happens in the last part of your small intestine and your colon, while UC occurs in the lining of your colon. Treatment includes anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, and medicine to slow the impact your immune system on your organs. Surgery is another possibility. It can often help with some of the symptoms and complications of the diseases, but it will not get rid of the underlying inflammation in the body that causes the IBD.
Lupus
This illness affects several parts of your body at the same time. Symptoms can include joint pain, sensitivity to light, kidney problems, extreme tiredness. You also might have a rash over your cheeks and nose. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and steroids can help you feel better, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may keep it from getting worse. If your symptoms are really bad, your doctor may suggest medication that slows down your immune system or chemotherapy (a combination of several powerful drugs).
Hashimoto’s Disease
If your thyroid doesn’t make enough of the hormones it is supposed to, it can lead to this illness which is also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis. It can make you gain weight, be more tired than usual, be sensitive to cold, and make your hair fall out, among other symptoms. You may notice that the front of your throat is swollen or your face is puffy. Medicine can replace these hormones and ease the symptoms.
Autoimmune Skin Disease
Skin conditions due to autoimmunity or immune dysregulation are not unique to people with primary immunodeficiency diseases. Common skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis are seen in people with normal immune systems as well.
Asthma
Asthma is a heterogeneous disorder characterized by chronic inflammation of the respiratory airways that can be triggered by allergen exposure or by other mechanisms, possibly autoreactive/autoimmune. The autoimmune hypothesis is further, indirectly, supported by the response to immunosuppressive drugs.
Most Common Autoimmune Disease Symptoms

Despite the varying types of autoimmune disease, many of them share similar symptoms. Common symptoms of autoimmune disease include:
- Fatigue
- Joint pain and swelling
- Skin problems
- Abdominal pain or digestive issues
- Recurring fever
- Swollen glands
Autoimmune Diseases and Controlling Inflammation

Most of these autoimmune diseases have no cure. Some require lifelong treatment to ease symptoms. The main panacea is to reduce inflammation.
Inflammation is a normal physiological defense against pathogen infection and tissue damage and quickly disappears under normal circumstances. However, in many chronic conditions, the inflammatory response continues and leads to significant tissue and organ damage.
Recently, increasing evidences have shown that the abnormal inflammatory response is closely associated with many chronic diseases, especially in autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), gout, and diabetes [1–3]. Although the importance of inflammatory dysregulation in chronic illnesses has been reported in recent studies, the pathogenesis of inflammation dysfunction in the autoimmune diseases remains elusive.
Reducing and Controlling Inflammation in Autoimmune Diseases
A. What are NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a class of drugs that reduce inflammation but are different from steroids which is another class of drugs that also reduces inflammation. NSAIDs reduce pain, fever, and swelling and are commonly prescribed for inflammation of the joints (arthritis) and other tissues, such as in tendinitis and bursitis. Examples of NSAIDs include aspirin, indomethacin, (Indocin), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Naprosyn),piroxicam (Feldene), and nabumetone (Relafen).

NSAIDs work by blocking the production of prostaglandins which are chemical messengers that often are responsible for the pain and swelling of inflammatory conditions.
Adverse Side effects:
The most frequently reported side effects of NSAIDs are gastrointestinal (stomach and gut) symptoms, such as feeling bloated, heartburn, stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and/or constipation. NSAIDS can also potentially cause ulceration and bleeding from the stomach and even the intestines. There are possibilities of renal side effects for prolonged use as well.
Cause of Inflammation COX-2 (CYCLOOXYGENASE-2)
COX-2 (Cyclooxygenase-2) is the enzyme largely responsible for causing inflammation, a common mechanism of disease.
Cyclooxygenase (COX) is a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of prostanoids, lipid signalling molecules that regulate various physiological processes in our body. COX2, one of the isoforms of COX, is highly inducible in response to a wide variety of cellular and environmental stresses. Increased COX2 expression is thought to play a role in the pathogenesis of many age-related diseases, including autoimmune diseases. The modulation of COX2 and its downstream signalling may be an approach for the intervention of autoimmune diseases.
B. What are Cox-2 inhibitors?
COX-2 inhibitors are a unique type of NSAIDs that selectively block the COX-2 enzyme and not the COX-1 enzyme. Blocking this enzyme impedes the production of prostaglandins by the COX-2 which is more often the cause for the pain and swelling of inflammation and other painful conditions of our body. Because they selectively block the COX-2 enzyme and not the COX-1 enzyme, these drugs are uniquely different from traditional NSAIDs which usually block both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes.
COX-2 inhibitors are prescribed concretely in inflammatory pathologies which is characterized by a prolonged pro-inflammatory status, including autoimmune diseases, metabolic syndrome, obesity, atherosclerosis, neurodegenerative diseases, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, arthritis, chronic inflammatory bowel disease and cardiovascular pathologies.
Celecoxib (Celebrex) is the only COX-2 inhibitor currently available in the United States.
Adverse Side Effects:
In last two decades numerous selective COX-2 inhibitors (COXIBs) have been developed and approved for various inflammatory conditions. However, data from clinical trials have suggested that the prolonged use of COX-2 inhibitors are also associated with life threatening cardiovascular side effects including ischemic heart failure and myocardial infection. Rofecoxib (Vioxx) and valdecoxib (Bextra) were withdrawn from the US market in 2004 and 2005, respectively, because they excessively increased the risk of heart attacks and strokes with long term use.
C. What Is a TNF Inhibitor?
TNF inhibitors are drugs that help stop inflammation. They are used to treat diseases like rheumatoid arthritis (RA), juvenile arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, plaque psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis, ulcerative colitis (UC), and Crohn’s disease.
They’re also called TNF blockers, biologic therapies, or anti-TNF drugs. There are many TNF inhibitors that have been approved by the FDA like Adalimumab (Humira), Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia), Etanercept (Enbrel), Golimumab (Simponi, Simponi Aria), Infliximab (Remicade).
How They Work
TNF inhibitors are antibodies made in a lab from human or animal tissue. Your body makes antibodies to fight off infections. Once they are introduced into your blood, they cause a reaction in your immune system which then blocks the inflammation.
Your immune system makes a substance called the tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Usually, your body keeps your TNF levels steady. But if you have an autoimmune disease like RA, something will go wrong. You will start making too much TNF, and that leads to inflammation.
TNF drugs may be given by injection under the skin at or by infusion over 2 to 4 hours in the hospital.
Adverse Side effects:
Some people develop serious allergic reactions. Because TNF inhibitors stamp down your immune system to stop inflammation, they can make it harder for you to fight off infections. You may be at a higher risk for getting colds, flu, urinary tract infections, or even tuberculosis (TB).
It is rare, but you also could be at higher risk of getting cancer if you take TNF inhibitors, including lymphoma or skin cancer. Some people may get serious brain reactions. Those with heart failure or multiple sclerosis shouldn’t take these drugs.
You should be aware that all vaccines have side effects which will affect the potency of the TNF medications because after you start taking them, your immune system could be diminished and compromised. One should not introduce get live viruses into the body while taking these drugs because of possible adverse reactions and they can interfere with how well the vaccines work.
Try CAVIARLIERI, a CAVIAR FOOD SUPPLEMENT to Control Inflammation in Autoimmune Diseases
Initial in- vivo research studies on Caviarlieri at the molecular level have proven that this caviar supplement is effective in the gene expression of genes related to anti-aging, inflammation (reduction in the expression of Cox2 gene), type 1 collagen and energy (GABPB1 gene).
By providing nutrition at the cellular level, Caviarlieri can trigger protein synthesis and prompt our bodies to produce proteins through active gene induction and thereby stimulating and accelerating cellular renewal and repair against damaged cells.
Mirroring the results of the Caviarlieri studies which are published in peer reviewed journals, in PubMed and Europe PMC, the current genetic expression studies (mRNA) on Caviarlieri show that this caviar supplement can potentially help to reduce and control inflammation and thereby alleviate the symptoms associated with autoimmune diseases. The studies show that the decrease in the expression of the COX2 gene after 60 days of treatment of Caviarlieri is up to 60-fold (p <0.001). This is extremely significant.
Taking Caviarlieri supplements over time can therefore activate the body’s own system in cellular renewal and repair against cellular damage through the genetic expression of COX-2.
Dr. Sotiris Nikolopoulos, Founder and Director of the Center for Molecular Analysis & Research S.A., responsible for the in vivo studies on Caviarlieri on genetic expression (mRNA) says that “Caviarlieri shows amazing anti-aging and anti-inflammatory results for patients from ages 18 to 83 years.”
His several studies confirm that Caviarlieri can potentially trigger epigenetics changes by providing nutrition at the cellular level and thereby provide benefits to those who consume it at a molecular, cellular and genetic level and potentially help to delay the onset and progression of degenerative diseases. This is unprecedented and is unheard of any other food supplement currently available.
Caviarlieri’s Significant Reduction of Inflammation and COX-2 genetic expression
INITIAL RESULTS
Reduction of COX2 Gene Expression with Caviarlieri
CAVIARLIERI intake significantly decreased the expression of the COX2 gene after 60 days of treatment up to 60-fold (p <0.001) in 5 individuals that presented with increased expression of COX2 compared to the rest of the participants as well as to COX2 gene expression of the control group. (Figures 4, 5, 6).
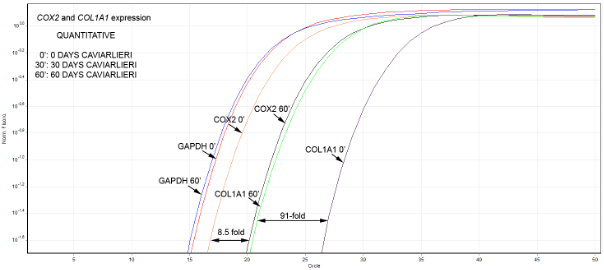
Figure 4a
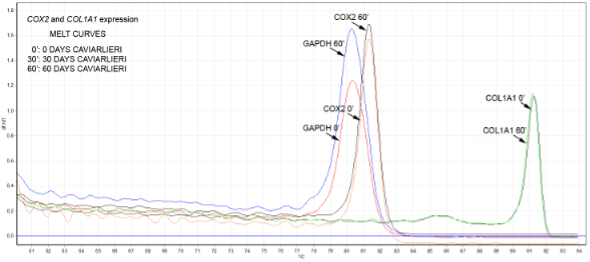
Figure 4b
FIGURE 4: Real-time PCR data for both COX2 and COL1A1 genes from blood samples collected at different time points from one participant and examined in the same run. With “0’” it is denoted the expression of the corresponding gene before CAVIARLIERI intake. With “30’” οr “60’” it is denoted the expression of the genes after 30 or 60 days on CAVIARLIERI respectively. The DNA synthesis and quantitation curves that correspond to each gene’s expression are shown (TOP). The melt curves that correspond to the expected and correct product for each gene examined are shown (BOTTOM). For this case a 91-fold increase in COL1A1 and an 8.5-fold decrease in COX2 gene was observed.
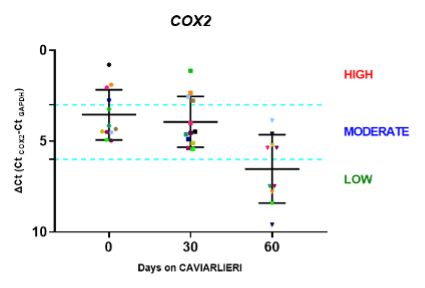
Figure 5
FIGURE 5: Graphical presentation of COX2 expression relative to housekeeping gene GAPDH (ΔCt (CtCOX2-CtGAPDH)), for all participants enrolled in CAVIARLIERI study. Each participant’s value is represented by a coloured dots. Circles represent COΧ2 expression values before CAVIARLIERI intake, squares represent COΧ2 expression values after 30days on CAVIARLIERI, triangles represent COΧ2 expression values after 60days on CAVIARLIERI.
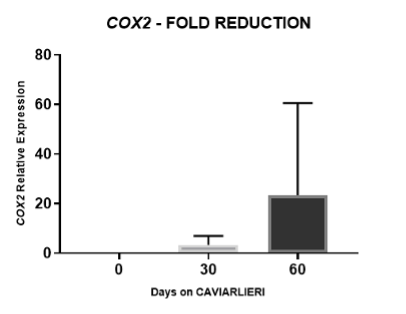
Figure 6
FIGURE 6: Relative expression change of COX2 gene in blood samples upon CAVIARLIERI intake. “0” represents the time before CAVIARLIERI intake, “30” represents the time after 30 days on CAVIARLIERI intake and “60” represents the time after 60 days on CAVIARLIERI intake. Values for each time point are presented as means +SEM of gene expression fold induction relative to 0 time values.
Caviarlieri’s Significant Reduction of Inflammation –TNF Alpha
Caviarlieri is also scientifically proven to help reduce the Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha which is an important inflammatory biomarker for metabolic syndrome conditions. In addition, Caviarlieri can also reduce the C-reactive protein (CRP), a blood test marker for inflammation in the body. CRP is classified as an acute phase reactant, which means that its levels will rise in response to inflammation.
The peer reviewed studies show that the intervention with Caviar DNA Extract (LD-1227) have shown in human chondrocytes that Caviarlieri could effectively inhibit IL-1β-induced proliferation and inflammatory reactions via inhibited activation of the transcription factor NF-κB pathway. Caviarlieri contains collagen elastin, protein and a rich array of other smaller unsaturated fatty acids. It is a Swiss Caviar Food Supplement formulated with the finest Caviar Cellular Extracts and marine peptides and highly polymerized collagen which have strong anti-inflammatory properties.
Patients with autoinflammatory disease such as gout and those with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARD), such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, antiphospholipid syndrome, ankylosing spondylitis and vasculitis among others, have increased prevalence of metabolic syndrome.
Note: Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions such as high blood pressure, high blood sugar, unhealthy cholesterol levels, excess abdominal fat that increases your risk of heart disease, stroke and type 2 diabetes.
Strong Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Caviarlieri
Published in Peer Reviewed Journal – Acta Bio Medical / Official Journal of the Society of Medicine and Natural Sciences of Parma Vol 84-53-60/2013
A sturgeon-derived bioactive compound beneficially modulates nuclear receptors controlling metabolic functions in patients with metabolic syndrome.
The aim of the study was to test the possible effects of a novel sturgeon-derived compound Caviar DNA Extract (LD-1227) on inflammatory markers related to metabolic nuclear receptors in patients with metabolic syndrome. The study population consisted of 76 patients with metabolic syndrome and 30 healthy subjects who were maintained to their current treatments and randomly supplemented with A) Caviar DNA Extract (LD-1227) (n=38) or B) placebo (n=38) as compared to C) healthy controls (n=30). Caviar DNA Extract (LD-1227) or placebo (water-soluble starch) were given daily at breakfast and dinner for three months.
At the end of the study period, as compared to B group, Caviar DNA Extract LD-1227-treated patients showed a significant improvement of all parameters (hs-CRP, IL-6, TNF-alpha) tested, irrespective of the presence of diabetes. Although the metabolic syndrome remains a multifaceted condition requiring a complex approach, Caviarlieri (LD-1227) could be a potential safe therapeutic tool to be integrated into a wider treatment and preventive medicine schedule strategy.
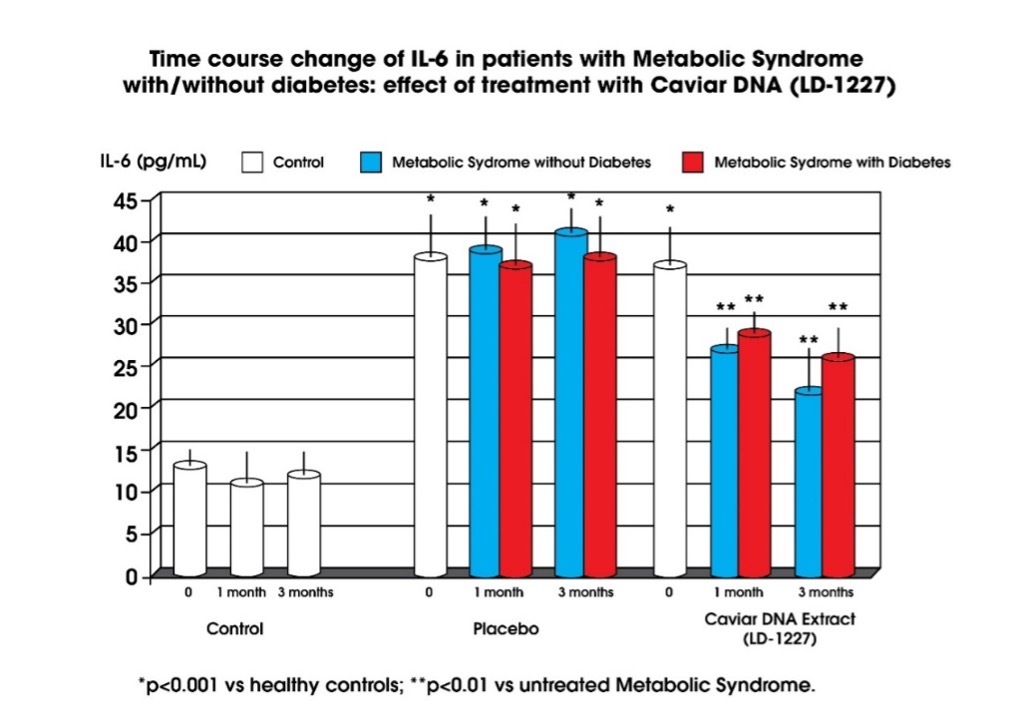
Figure 1a. Time course change of IL-6 In patients with Metabolic Syndrome with/without diabetes: effect of treatment with Caviar DNA Extract (LD-1227). Throughout the whole study, the level of IL-6 was significantly higher in Metabolic Syndrome patients as compared to healthy controls and it was not affected by the presence of diabetes (p<0.05, fig 1).
After intervention with Caviar DNA Extract (LD-122), IL-6 level decreased significantly in all Metabolic Syndrome patients (p<0.05 vs baseline and vs placebo group).
Note: Interleukin-6 is a cytokine not only involved in inflammation and infection responses but also in the regulation of metabolic, regenerative, and neural processes.
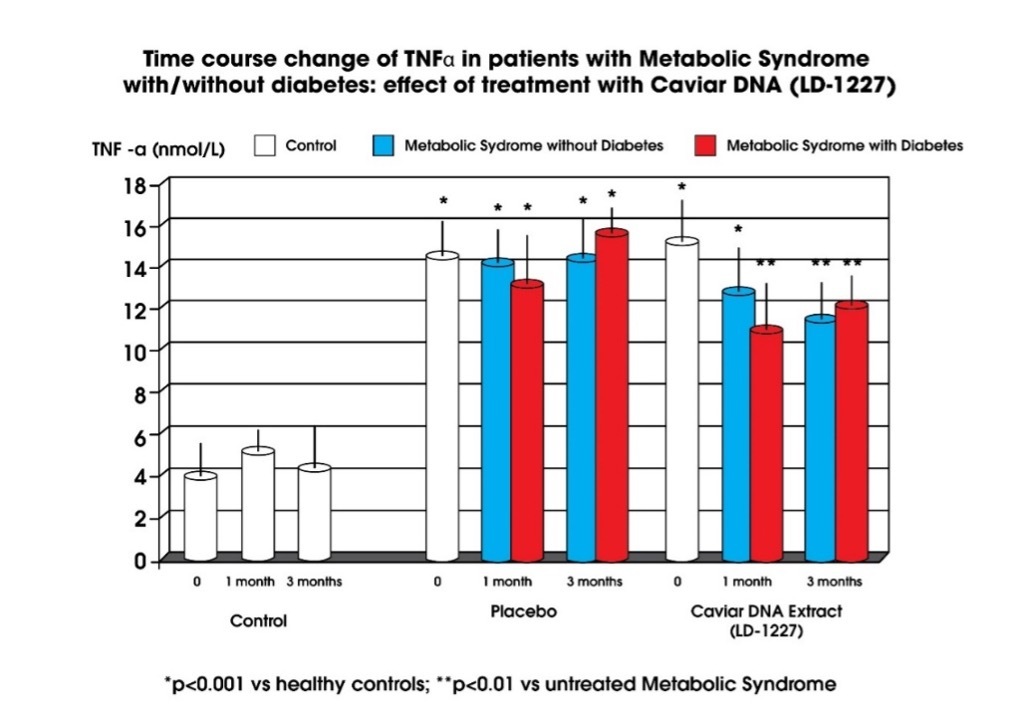
After intervention with Caviar DNA Extract (LD-1227), TNF-α level (inflammation) decreased significantly in all Metabolic Syndrome patients (p<0.05 vs baseline and vs placebo group).
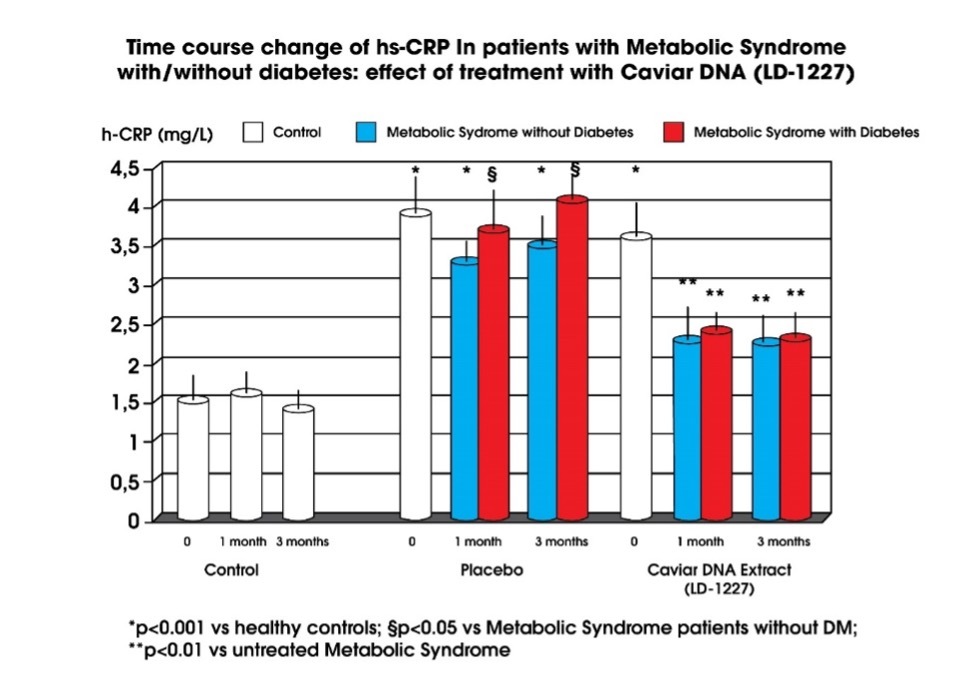
The level of hs-CRP in patients with Metabolic Syndrome was significantly higher than in healthy controls (p<0.05, fig 2) and particularly in those with overt diabetes (p<0.05 vs MS patients without diabetes). After intervention with Caviar DNA Extract (LD-1227), hs-CRP significantly decreased (p<0.05 vs placebo).
Note: C-reactive protein (CRP) is a blood test marker for inflammation in the body. CRP is produced in the liver and its level is measured by testing the blood. CRP is classified as an acute phase reactant, which means that its levels will rise in response to inflammation.
A high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) test, which is more sensitive than a standard test, also can be used to evaluate your risk of developing coronary artery disease, a condition in which the arteries of your heart are narrowed. Coronary artery disease can lead to a heart attack.
Conclusion
The intervention with Caviar DNA Extract (LD-1227) has shown in human chondrocytes that this sturgeon-derived compound could effectively inhibit IL-1β-induced proliferation and inflammatory reactions via inhibited activation of the transcription factor NF-κB pathway. Caviarlieri contains collagen elastin, protein and a rich array of other smaller unsaturated fatty acids, and structural phospholipids which may exert a synergistic action on multiple mechanisms of the inflammatory cascade.
Caviarlieri is backed by Science
Prior to the recent studies on mRNA and genetic expression, Caviarlieri already has several Peer Reviewed Scientific Studies published in PubMed and PMC Europe. The benefit claims are therefore evidence based, like significant increase in energy levels, mood elevation, reduction in joint pain, enhancement of sleep quality, improving brain health, strong anti-inflammatory properties and many others. It is important to remember that healing begins at the cellular level. These studies demonstrate Caviarlieri’s effective therapeutic outcomes and its ability to modulate and modify disease-related processes.
Why is Caviarlieri a safe and potent option to manage Autoimmune diseases?
NO SIDE EFFECTS

Caviarlieri is NOT A DRUG but a potent oral food supplement approved by the Swiss Public Health Authority. Unlike drugs or medications, there are no side effects for long term use. Caviarlieri is on the Cologne List® that publishes products which have been tested for selected doping substances by one of the globally-leading laboratories in nutritional supplement analytics.
Manufactured using the Swiss Cold Process Extraction Technology, Cellularix, Caviarlieri comes in a soft gel form and is made of peptides, encapsulating the Caviar bioactive nutrients and marine peptides for optimal absorption. It is important to remember that not everything we consume can be absorbed by the body.
By providing essential nutrition at the cellular level, Caviarlieri triggers protein synthesis, genetic expression (mRNA) and thereby stimulates our own body system to heal, repair and renew our cells at an accelerated rate against damaged cells. Unlike drugs, it will take a 3-6 months regime for the cellular healing and repair to generate maximum benefits and results.
Caviarlieri is available in the leading Swiss Medical Centres and Luxury Spas as well as Pharmacies throughout Switzerland.
Subject
Recent Posts
-
The Amazing Benefits of Highly Polymerized Fish Collagen Peptides with Elastin – Caviarlieri
-
The World’s Most Effective Caviar DNA Extract with Marine Bioactive Peptides
-
Are Supplements effective for Joint Pain?
-
Why Is Sustainable Immunity Important for Your Long-Term Health
-
What is your “Body Age” – Biological Age?




