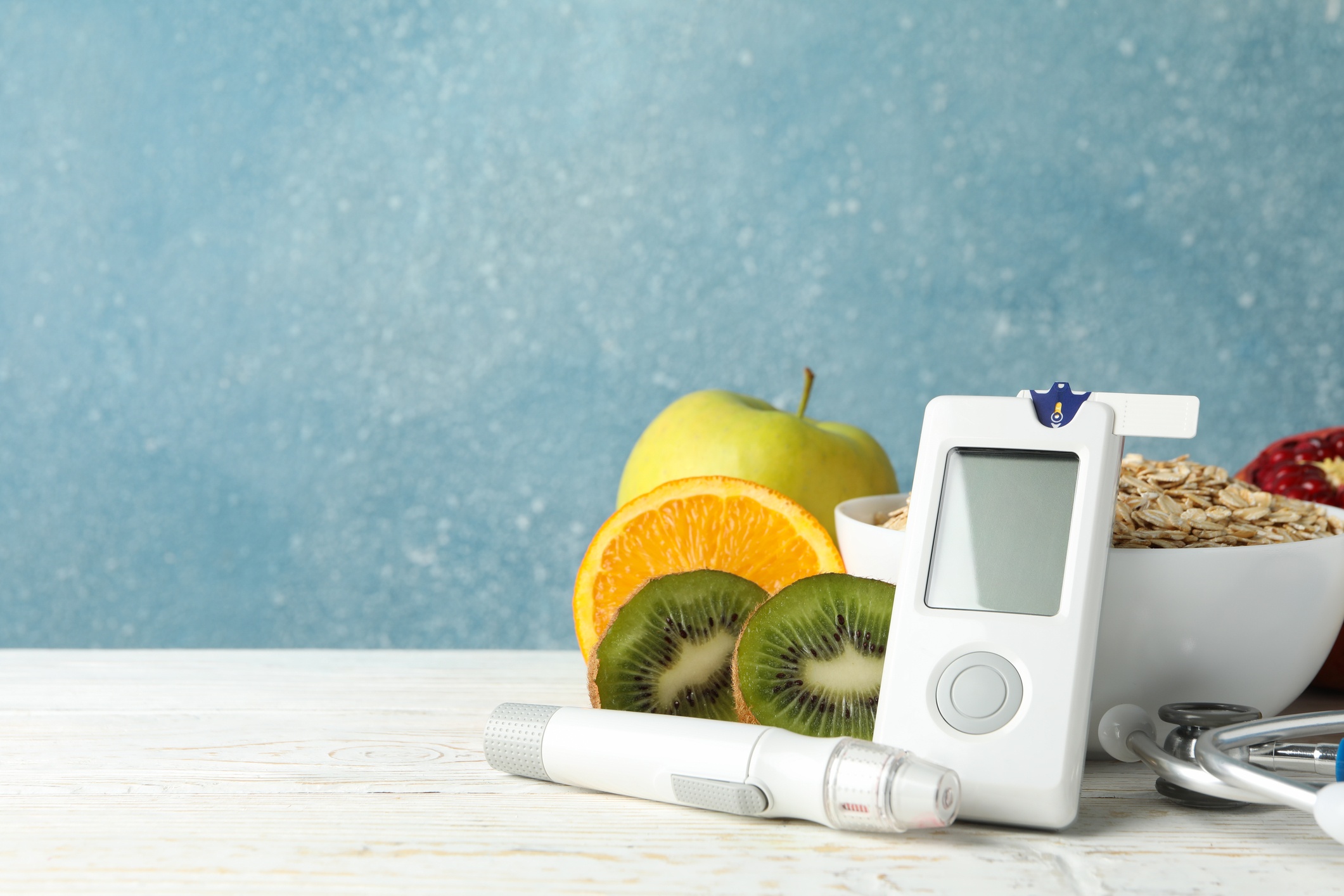
Glycemic Index, Blood Sugar Control and Diabetes
Caviarlieri | Published June 24, 2020
Introduction to Glycemic Index
What is Glycemic Index? If you have not gone on a serious diet modification programme, this term may be quite unfamiliar to you. The glycemic index is a measurement system that assigns a number or score to foods with carbohydrate content and how much each type of food converts the carbohydrate content into blood sugar. The score ranges from zero to 100. The smaller the number, the less it increases our blood sugar and the better it is for our body. If the score is less than 55, it is considered low because these foods are more slowly digested and absorbed and hence a low and slow rise in blood sugar which is good. A medium bracket level follows with a score below 69 while any number above that is considered high which automatically means it rapidly converts and increases the blood glucose in a short amount of time and it is not good for our body.
Purposes of Glycemic Index

The glycemic index is mainly used as a guidance tool for diet plans or food choices. Those who commonly use the Glycemic Index are those who aim to lose weight or maintain a healthy weight through dieting, those who wish to have more knowledge in eating healthier meals, and Diabetics who need to follow a certain diet as a vital part of their treatment plan. The Glycemic Index has proven to be helpful to these goals especially for those who have particular issues or unhealthy health conditions.
Importance of Blood Glucose Control
Controlling our blood glucose levels is one of the most important ways to keep our bodies healthy and prevent many diseases but it is one of the hardest things to do or follow due to the nature of the food that is available nowadays. Blood glucose is defined as the sugar in our blood that is used to supply energy to the cells. Eating habits should be considered as a means to maintain energy levels without causing spikes or sudden decreases in the blood sugar which is not good to our body. Controlling our blood glucose not only means regulating it from being constantly high but also from being too low as both can be dangerous. Apart from the most common link to blood glucose, which is Diabetes, there are other conditions in our body that would benefit from blood sugar control such as those with pancreatitis, thyroid problems, Cushing’s syndrome, and pregnant women and their complications.
Ways to Control Blood Sugar
There are many ways to effectively keep our blood sugar in check. These methods are common, in fact, being repeated over and over again for disease prevention and for an overall regimen to keeping our bodies generally healthy. Apart from the obvious which is watching what we eat and avoiding high-carbohydrate foods, here are other important ways and how they work.
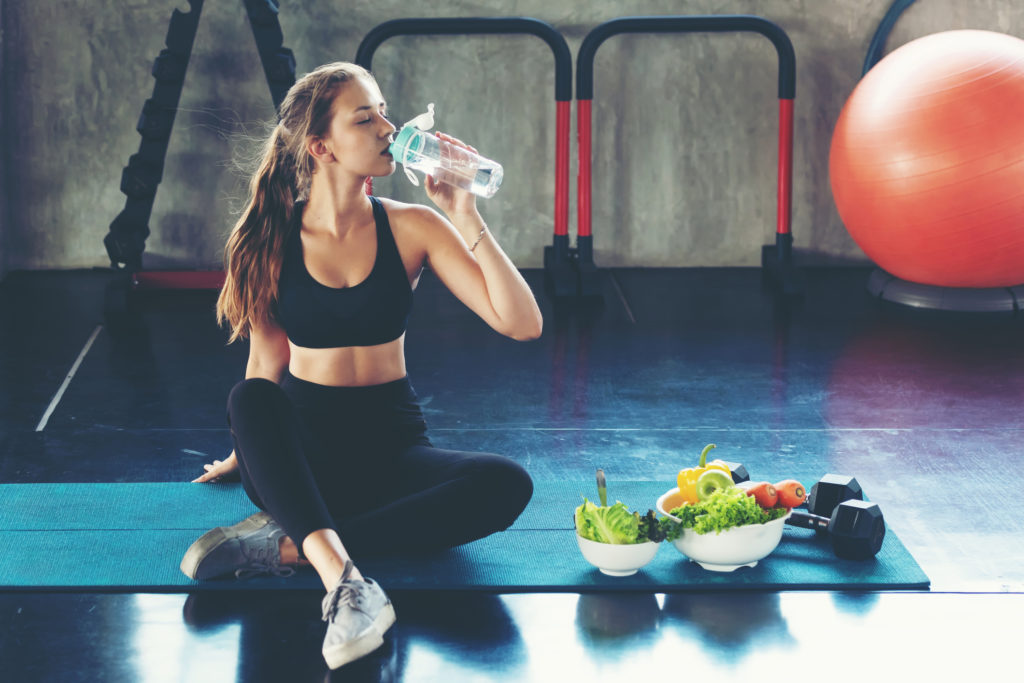

- Exercising regularly. Being physically active not only helps lose unwanted weight but also increases our sensitivity to insulin which means that our cells use the sugar in the blood more efficiently. As the muscles contract during exercise, more blood sugar is used for energy. Whatever exercise that gets the heart rate up and makes the body work against resistance are good forms of exercise.
- Eat more fiber-rich food. Fiber helps slow down the digestion of carbohydrates and absorption of the sugar from it. Since it also isn’t completely broken down by the body, it does not affect blood sugar that much.
- Keep hydrated by drinking water. Water helps flush the extra blood sugar from the kidneys through the urine. Studies have shown that those who regularly drink more water have a lower risk of having high levels of blood sugar.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a condition wherein the body is unable to utilize the sugar (glucose) in the blood through Insulin. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas and is responsible for regulating blood glucose by transporting it to cells in the body that needs energy. The problem arises when there is not enough insulin or none at all or when the body has developed a resistance to insulin, and this is differentiated in the two types of Diabetes. However, considered a serious condition due to the possible complications and long-term effects, Diabetes is highly manageable.
Diabetes and the Glycemic Index
Food choice plays a big role in a Diabetic’s life. The Glycemic Index can be used as a guide for diabetics in the area of meal planning as it classifies food according to their ability to raise blood sugar. However useful, the Glycemic Index cannot be used simply at face value nor is it complete. The following are the things to consider in understanding how it fully affects one’s diet.
- Food which are cooked may potentially increase the Glycemic Index. This is the case for pasta. When pasta is cooked al dente, it has a lower GI compared to if it is cooked more to a softer texture.
- Fresh versus processed food. Fruit juice that has been processed contains a higher GI than fresh fruit juice.
- Ripe fruits have a higher GI score.
- Food rich in fiber and high in fat may lower the overall Glycemic Index score.
- Combination of food taken in a meal can affect the GI.
- Some foods high in GI have nutrients that lower the overall GI. A balance is still essential in meal planning for Diabetics.
Blood Glucose Control in Diabetics
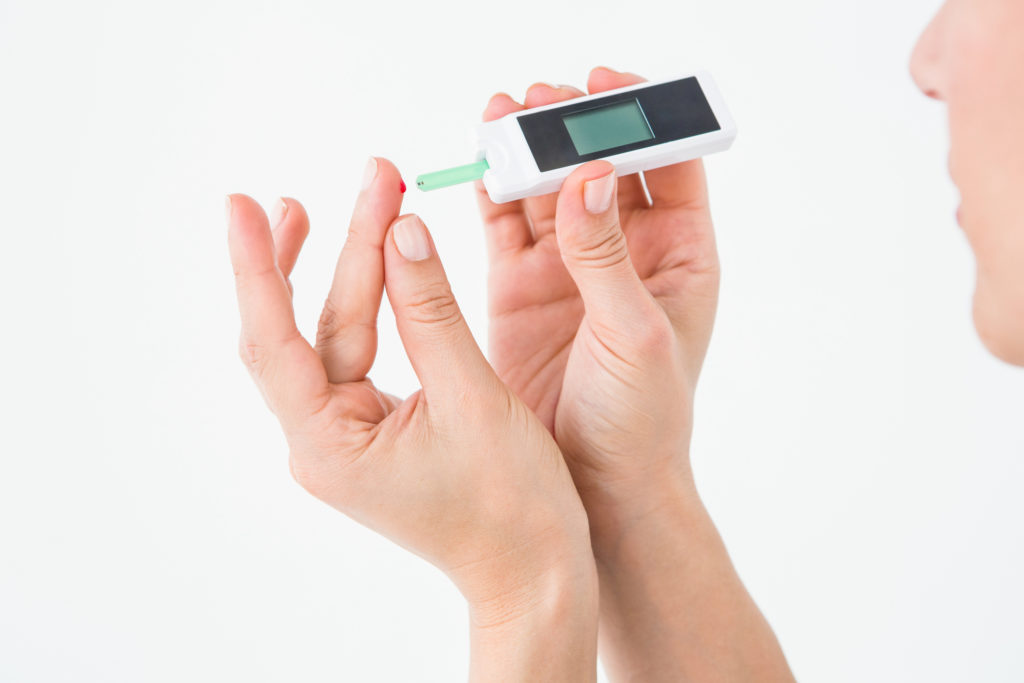
Watching or monitoring of blood glucose levels is a more serious business for Diabetics than it is for those who do not have the disease. Proper monitoring of blood glucose in Diabetes is a commitment as it is one’s way to prevent complications. Significant damage or health problems can arise from a single episode of uncontrolled hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia as it may lead to a heart attack or stroke, irreversible kidney damage, vision problems, circulation and scarring in blood vessels and many more. Fortunately, blood glucose meters are now available as self-testing kits. More importantly, blood sugar monitoring should start from one’s commitment to diet modification, changing lifestyle and habits and not merely checking. Nowadays, there are many other tools to equip Diabetics such as the glycemic index to help guide and educate on how food can be harmful or helpful. This goes the same for people without diseases but would like to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Subject
Recent Posts
-
The Amazing Benefits of Highly Polymerized Fish Collagen Peptides with Elastin – Caviarlieri
-
The World’s Most Effective Caviar DNA Extract with Marine Bioactive Peptides
-
Are Supplements effective for Joint Pain?
-
Why Is Sustainable Immunity Important for Your Long-Term Health
-
What is your “Body Age” – Biological Age?




